02.21.39.247 Contact us
Featured


How an Electric Heating Product Warms Your Space (and Which One Is Right for You)

When building or renovating your home and choosing an electric heating system, it is natural to ask yourself a few key questions: “Which heating system is right for me?”
Among the available options, which one will have the lowest impact on your energy bill? And how can you achieve a good level of thermal comfort? To answer these questions correctly, it is essential to understand how different electric heating systems work and how they distribute heat within a room.
What is heat and how it spreads
Main types of electric heating
Electric convector heater
Radiant panel
Dual-Therm electric radiator
How to choose the product that best fits your needs
Main types of electric heating
Electric convector heater
Radiant panel
Dual-Therm electric radiator
How to choose the product that best fits your needs
What is heat and how it spreads
Heat is a form of energy transfer. There are essentially three ways in which it is transmitted.
Thermal conduction
Heat is transferred through direct contact between two bodies, such as when a hot object warms a colder surface.
Thermal convection
This is the natural phenomenon whereby warm air rises while cold air sinks. In domestic heating, warm air moves upwards while colder air settles near the floor.
Radiation
Heat is transmitted in the form of electromagnetic waves (typically in the infrared spectrum), without direct contact. This is the type of heat we feel when approaching a warm source.
Understanding how heat spreads is essential in order to identify the electric heating system best suited to your needs.
Main types of electric heating
Terms such as “convector”, “radiant panel” and “radiator” are often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to very different devices.
- Electric convector: heat generated through convection
- Radiant panel: heat emitted through infrared radiation
- Electric radiator: combined convection and radiant heat
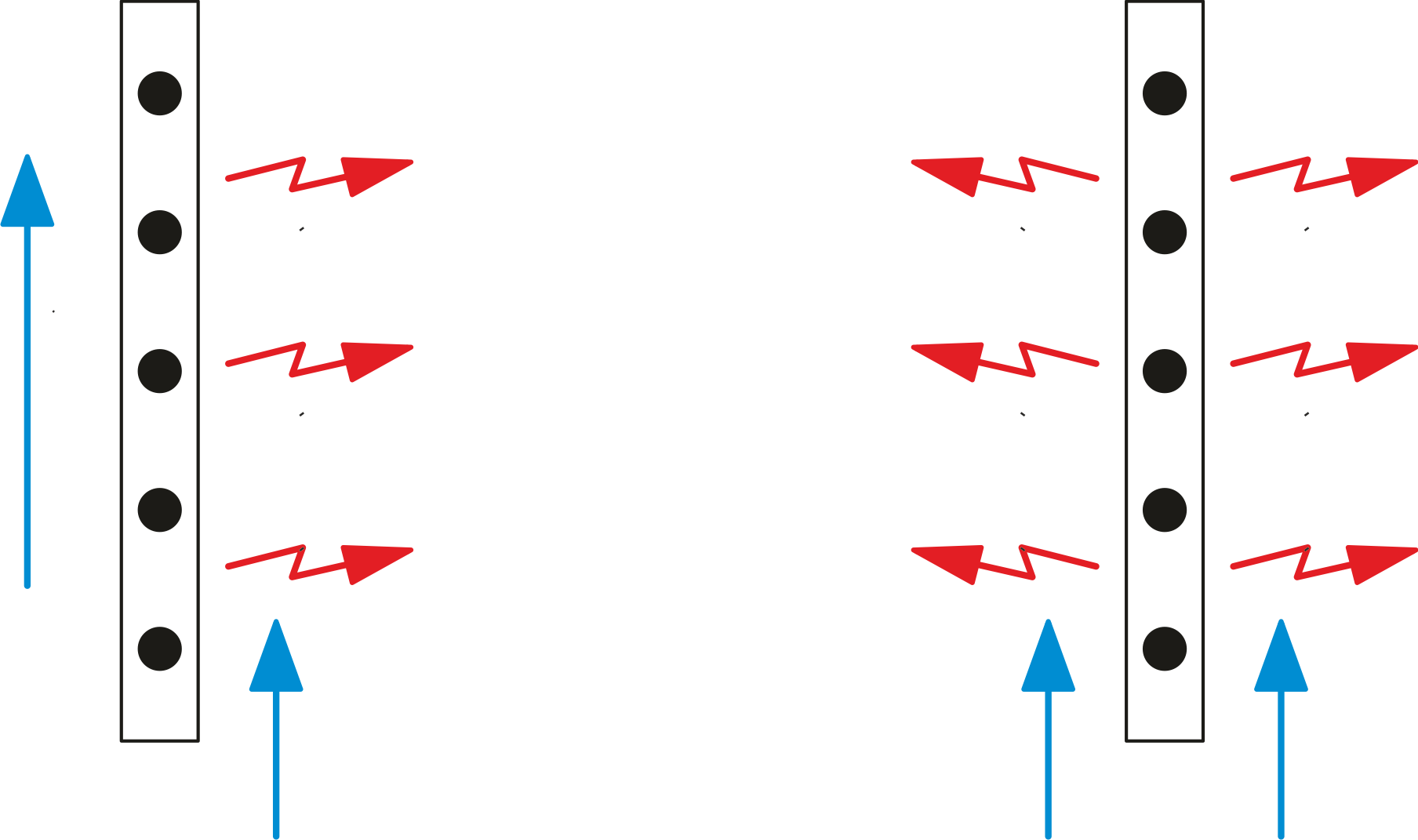
Electric convector heater
Heating through natural convection
The electric convector is one of the simplest and most traditional heating solutions. Its operation is based on the natural convection of air.
Cold air enters from the lower part of the unit, is heated by an electric element, and exits through the upper grille.
This process happens quickly and allows heat to spread rapidly throughout the room.

Radiant panel
Infrared radiant heating
Radiant panels generate and transmit heat through infrared radiation, which directly warms the human body as well as walls, furniture and objects, which in turn re-emit the heat.
The perceived effect is similar to sunlight: heat is distributed evenly, without air movement and without noise.
This helps prevent overheated areas or localized cold spots within the room. Depending on the model, heat can be emitted from one or both sides.

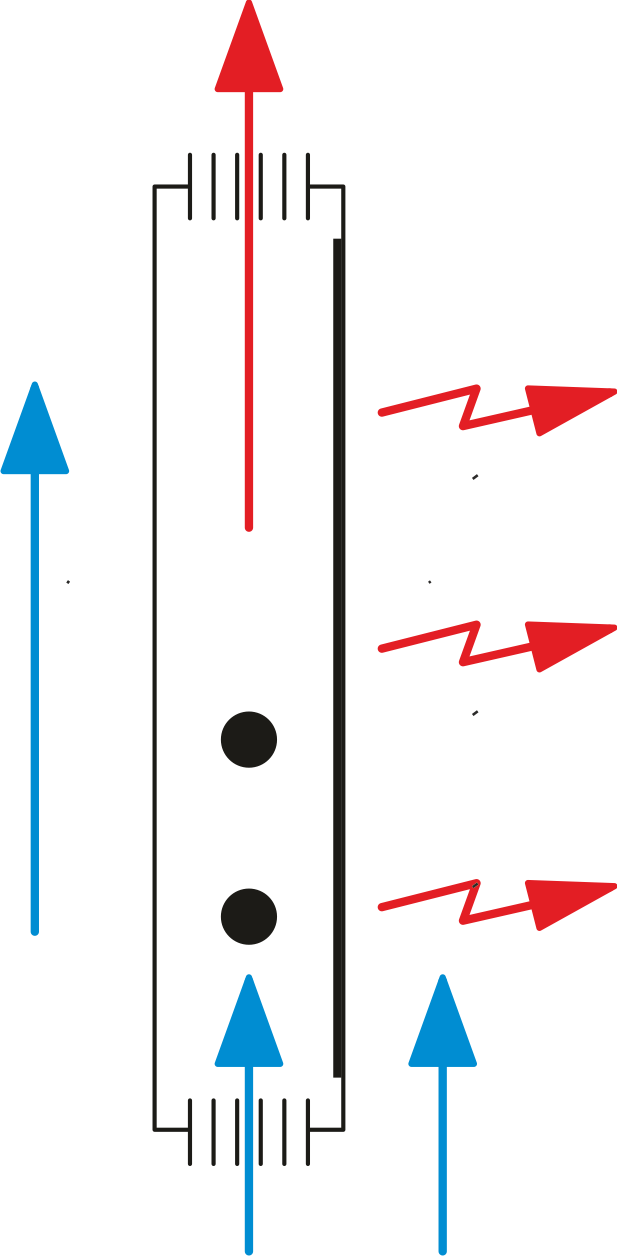
Dual-Therm electric radiator
Combined convection and radiation
Dual-Therm electric radiators combine two heat diffusion methods: an initial convection phase, which quickly brings the room up to temperature, followed by radiant heating, which helps maintain it over time and ensures optimal comfort. Once the desired temperature is stable, the convective component can be reduced, leaving room for radiant heat.

How to choose the product that best fits your needs
Now that you are familiar with the main types of electric heating, you can make a more informed choice when selecting the most suitable product for your home.
The ideal solution depends on room size, usage patterns and the level of thermal comfort you want to achieve.
Need help choosing? Contact us for a personalised consultation!